What is the "?." JavaScript/TypeScript operator
In JavaScript and TypeScript, the “?.” operator is called optional chaining.
It works in a similar fashion to the . (chaining) operator, except that it short-circuits instead of causing an error when a value is null or undefined.
That means const obj = {}; console.log(obj.hello?.world); will log undefined (the value of obj.hello) instead of throwing a TypeError: obj.hello is undefined that console.log(obj.hello.world); would cause.
Table of Contents
Using “?.” (optional chaining) in JavaScript/TypeScript
“?.” (optional chaining) can be used in the following environments.
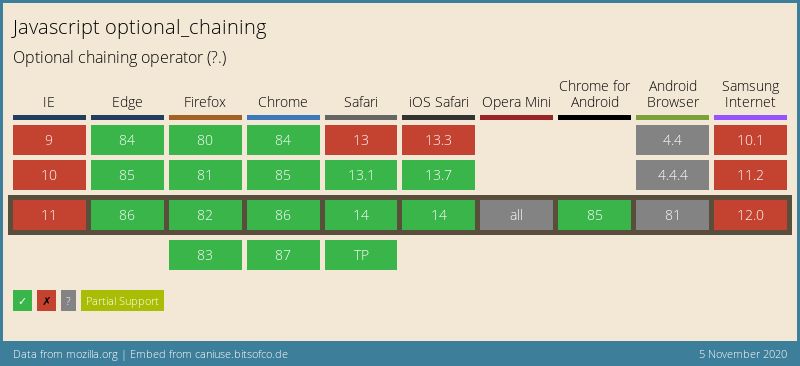
Browser Support as of 5th November 2020, see the compatibility table on MDN. It’s been supported since Chrome/Chrome for Android/Edge 80, Firefox 74, Safari 13.1, Safari for iOS 14.
“?.” (optional chaining) is also supported in Node 14+
“?.” (optional chaining) in unsupported environment
“?.” (optional chaining), can be compiled for use in unsupported environments. These include Node <14 (12, 13), Internet Explorer 11, Firefox/Opera for Android and Samsung Internet.
It can be compiled using Babel:
- as part of babel-preset-env v7.8.0+
- with the babel-plugin-proposal-optional-chaining
TypeScript 3.7+ includes optional chaining (?.) syntax transformation.
Examples of “?.” (optional chaining) in JavaScript/TypeScript
A simple example of the optional chaining (?.) operator is the following, where we have a user variable, that can be null/undefined and we want to access the username:
function getUserName(user) {
return user?.name
}
Without optional chaining, we would have done something like the following:
function getUserName(user) {
return user && user.name;
}
Optional chaining (?.) can also be useful when access the DOM, for example, accessing an input’s value in JavaScript, in this case, thanks to optional chaining (?.) event if an input with name=email is not found, the application will not crash, we’ll just get inputValue set to null.
const inputValue = document.querySelector('input[name=email]')?.value;
The equivalent scenario in TypeScript would be:
const inputValue: string = document.querySelector<HTMLInputElement>('input[name=email]')?.value;
Interested in Alpine.js?
Power up your debugging with the Alpine.js Devtools Extension for Chrome and Firefox. Trusted by over 15,000 developers (rated 4.5 ⭐️).
orJoin 1000s of developers learning about Enterprise-grade Node.js & JavaScript